Note
Click here to download the full example code
Galaxy Ellipticity Distributions¶
This example demonstrate how to sample ellipticity distributions in SkyPy.
3D Ellipticity Distribution¶
In Ryden 2004 1, the ellipticity is sampled by randomly projecting a 3D ellipsoid with principal axes \(A > B > C\).
The distribution of the axis ratio \(\gamma = C/A\) is a truncated normal with mean \(\mu_\gamma\) and standard deviation \(\sigma_\gamma\).
The distribution of \(\epsilon = \log(1 - B/A)\) is truncated normal with mean \(\mu\) and standard deviation \(\sigma\).
The func:skypy.galaxies.morphology.ryden04_ellipticity() model samples
projected 2D axis ratios. Specifically, it samples the axis ratios of the
3D ellipsoid according to the description above [1] and
then randomly projects them using
skypy.utils.random.triaxial_axis_ratio().
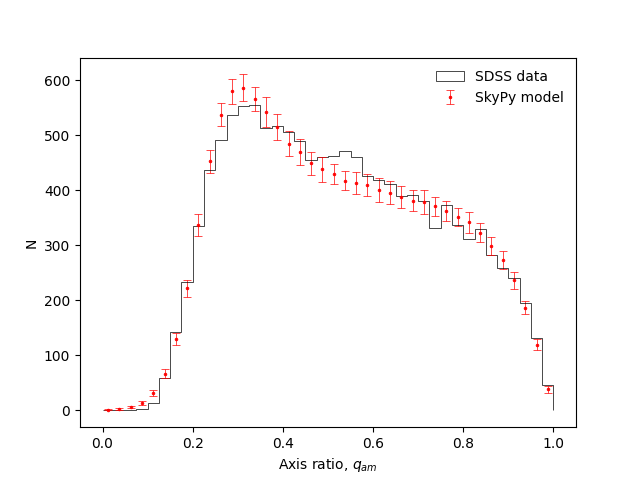
Validation plot with SDSS Data¶
Here we validate our function by comparing our SkyPy simulated galaxy
ellipticities against observational data from SDSS DR1 in Figure 1 [1].
You can download the data file
SDSS_ellipticity,
stored as a 2D array: \(e_1\), \(e_2\).
In this example, we generate 100 galaxy ellipticity samples using the
SkyPy function
skypy.galaxies.morphology.ryden04_ellipticity() and the
best fit parameters
given in Ryden 2004 [1]:
\(\mu_\gamma =0.222\), \(\sigma_\gamma=0.057\), \(\mu =-1.85\)
and \(\sigma=0.89\).
from skypy.galaxies.morphology import ryden04_ellipticity
# Best fit parameters from Fig. 1 in Ryden 2004
mu_gamma, sigma_gamma, mu, sigma = 0.222, 0.057, -1.85, 0.89
# Binning scheme of Fig. 1
bins = np.linspace(0, 1, 41)
mid = 0.5 * (bins[:-1] + bins[1:])
# Mean and variance of sampling
mean = np.zeros(len(bins)-1)
var = np.zeros(len(bins)-1)
# Create 100 SkyPy realisations
for i in range(100):
# sample ellipticity
e = ryden04_ellipticity(mu_gamma, sigma_gamma, mu, sigma, size=Ngal)
# recover axis ratio from ellipticity
q = (1 - e)/(1 + e)
# bin
n, _ = np.histogram(q, bins=bins)
# update mean and variance
x = n - mean
mean += x/(i+1)
y = n - mean
var += x*y
# finalise variance and standard deviation
var = var/i
std = np.sqrt(var)
We now plot the distribution of axis ratio \(𝑞_{am}\)
using adaptive moments in the i band, for exponential galaxies in the SDSS DR1
(solid line). The data points with error bars represent
the SkyPy simulation:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.hist(q_amSDSS, range=[0, 1], bins=40, histtype='step',
ec='k', lw=0.5, label='SDSS data')
plt.errorbar(mid, mean, yerr=std, fmt='.r', ms=4, capsize=3,
lw=0.5, mew=0.5, label='SkyPy model')
plt.xlabel(r'Axis ratio, $q_{am}$')
plt.ylabel(r'N')
plt.legend(frameon=False)
plt.show()
References¶
- 1
Ryden, Barbara S., 2004, The Astrophysical Journal, Volume 601, Issue 1, pp. 214-220
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.517 seconds)